Guinea pigs are very social and tend to be a little higher maintenance than other small pets.
They are small, gentle, personable, and fun. They are a companion animal and do require special care and attention.

Supplies
This is a brief list of recommended supplies. See some of our favorites at the bottom of this page.
- Appropriate size housing (see below for details)
- Fleece & or washable, soft potty pads
- Potty-box *no grates
- Hay bag/feeder
- Food dish
- Water bottle
- Supply of hay
- Supply of high-quality pellets (no seeds/colored additives)
- Vegetables (see below for safe veggies)
- Supply of potty pellets/bedding (no wood chips – some are toxic)
- Assorted toys
- Hidey hut/tunnel
- Animal carrier
- Nail trimmer
Housing
Must be indoor! Avoid aquariums and plastic tubs due to poor ventilation and these are much too small.
Bigger is better
Start with a cage and line it with fleece and/or washable, soft potty pads (absorbent bedding). (No grates – hard on feet)
Min size 2′ x 3′ for 1-2 piggies (2′ x 4′ preferred).
- One guinea pig: 7.5 square feet, or about 30-by-36 inches, is the bare minimum recommended, but bigger is better. (Guinea pigs are highly social, so it is best to have at least two guinea pigs who get along with each other.)
- Two guinea pigs: 7.5 square feet (minimum), but at least 10.5 square feet (30” x 50”) is preferred.
- Three guinea pigs: 10.5 square feet (minimum), but at least 13 square feet (30” x 62”) is preferred.
- Four guinea pigs: 13 square feet (minimum), but at least 30-by-76 inches is preferred.
1) C&C Cages: Most common. Flexible, expandable, you control the design. Can be enclosed. More examples here 

Build Your Own: Wire Cube Storage (example here) & Coroplast (at stores like Menards or on Amazon – example here)
Ideas from Kavee here:
2) Midwest Guinea Pig Cage: Expandable. Completely enclosed. Found here
3) Exercise Pen if unable to fit through the bars (example here)
Benefits of Larger:
- Enrichment: Most basic type of enrichment you can provide. Without adequate stimulation, guinea pigs may become bored and depressed.
- Exercise: Adequate room to exercise which can help prevent some medical conditions.
- Peaceful co-existence: Larger areas increase the liklihood of peaceful co-existence amount multiple guinea pigs.
- Easier to clean: Less build up of waste and space to separate bathroom ares from other activities.
- Happier: Opportunity to express a wider range of natural behaviors with room to run, binky, and explore.
Location:
- Near you, like the living room if this is where you spend most of your time. Guinea pigs enjoy being near family activity and benefit from more attention when they are easy to see and hear.
- Provide hidey spot(s). Make sure they have a place to retreat for quiet time if they need it.
- Temperature 65-75 F and away from vents.
Hot temperatures are very dangerous for guinea pigs because they cannot sweat to cool down, making them prone to heatstroke at temps above 78 F. While they can deal with short-term low temps, high temps can kill them. - Noise. Do not place them near a stereo, TV, etc. or other loud noises due to sensitive hearing.
- Safety. Away from kitchens/cooking areas, safe from predators and children, away from scents (candles/plug ins). NEVER outside.
Guinea Pig Diet
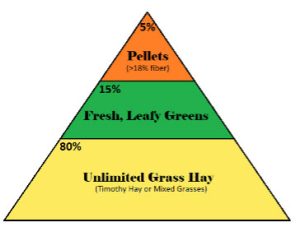 *GI stasis is a quickly fatal issue that commonly results from poor diets (see information below)
*GI stasis is a quickly fatal issue that commonly results from poor diets (see information below)
Hay
Grass hay makes up 80% of a guinea pig’s diet and must be available in unlimited quantities at all times. Hay is essential to good health. Hay stimulates the guinea pig’s GI tract to work correctly and helps prevent blockages in the GI tract and dental issues by keeping teeth trimmed. Grass hay is rich in Vitamin A and D, calcium, protein, and other nutrients.
IMPORTANT: Before introducing any fresh foods, it is best if your guinea pig has been eating grass hay well, first. The grass hay will help to get your guinea pig’s GI tract motility and flora in good working order so that he/she will be able to accept new foods more easily.
Provide a variety of fresh, grass hay daily as it provides natural foraging to find the best pieces. Your rabbit will dig through the hay to find the best pieces to eat; therefore, never consider what they don’t want to eat “wasted hay.” Varying the type of grass hay or mixing hays is a great idea (e.g., timothy, orchard, oat hay, brome, etc.). Alfalfa is not grass, but rather a legume (in the pea and bean family) and is only safe for guinea pigs under 6 months of age.
Store hay in dry, temperature-controlled climates out of plastic to prevent mold.
Water
Fresh water must be supplied daily. Water is necessary to flush excess calcium from the kidneys and bladder, and it is essential for healthy function of the gut and its bacteria.
Pellets & Supplements
Pellets should be fresh and should be high in fiber and have additional vitamin C in them specific to guinea pig needs, not rabbits. Guinea pigs do not produce their own Vitamin C. Supplement to help prevent illness/disease, such as scurvy.
Check dates – pellets should be purchased and used within 3 months of being made. Vitamin C levels decrease as pellets age which is why a “Vitamin C cookie” daily is recommended (example here).
Amounts and pellet grass type are based on age: In general, most adult guinea pigs get 1/4 to 1/8 cup a day. Replace pellets daily.
Alfalfa pellets are good for young guinea pigs <6 months old. At 6 months of age, pellets transition to timothy. Alfalfa can lead to kidney stones from too much calcium.
- Young (under 6 months): Unlimited alfalfa pellets to support rapid growth.
- Adult (over 6 months): Generally 1/8 to 1/4 cup a day. Consult a vet on diet for your specific guinea pig(s).
Pellets should NEVER have colored pieces or seeds in them. Always check the ingredients. Many companies sell “adult pellets” that are not timothy based and have poor ingredients in them.
Vegetables
*Only introduce 1 new food at a time. Wait 3-4 days between new foods to allow the intestinal tract to adjust.
Research before feeding anything. This is not an all-encompassing list of safe foods and there are dangerous foods to guinea pigs.
1/4 cup (packed) daily of Vitamin C rich vegetables:
Cilantro
Green Leaf Lettuce
Mustard Greens
Red Leaf Lettuce
Romaine Lettuce
Turnip Greens
Vegetables high in vitamin C that are good in small amounts:
Brocolli
Red/Green Pepper
Vegetables high in vitamin C that are ok in small amounts 1-2 times per week:
Carrots
Tomato
Zuccini
Parsley
Spinach
Fruit
Limit fruits very small amounts, used as an occasional treat/up to a few times a week. Fruit is high in sugar. Example: Small wedge of apple, few blueberries, thin slice of banana.
Introduce new fruits slowly to avoid diarrhea.
High in Vitamin C: Kiwi, Strawberries (high in oxilates), and Citrus (e.g., oranges).
*No frozen fruit
Treats (Optional)
Many pet stores sell treats disguised as “healthy” choices; most of these are fat- and sugar-rich and are not healthy at all. Commercial treats are unnecessary and a waste of money.
Use daily/weekly amounts of veggies/fruits as treats or provide activities like hay in a cardboard tube.
GI Stasis
Emergent, potentially fatal within 24-48 hours
Immediate recognition is important (e.g., refusing a favorite food, decreased poops, etc.)
Know what to do. See more information here.
Resources:
- Guinea Pig Cage Company: www.guineapigcagecompany.com
- Humane World for Animals: www.humaneworld.org
- Kavee: www.kavee.com
- VeterinaryPartner.com

